Release Date:2022-10-09 Views: 39
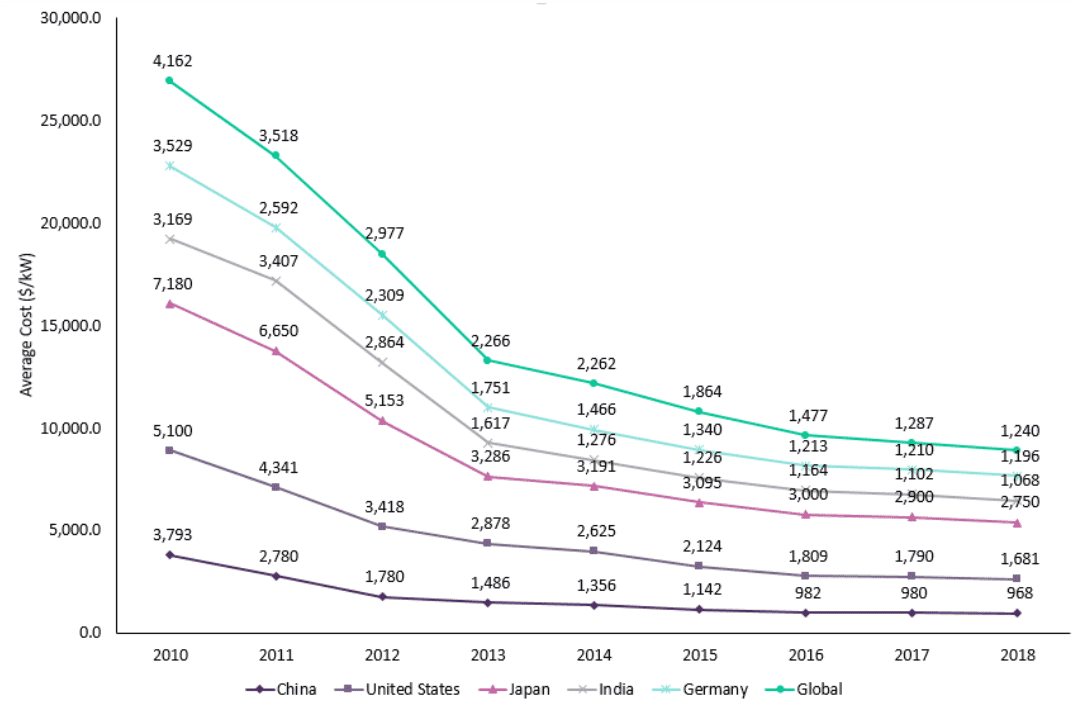
Solar energy is the cleanest and richest renewable energy available. Solar photovoltaic cells or panels are devices that convert solar energy into electrical energy. Intensive development and large-scale production of solar panels have begun in this new millennium. In 2018, the global installed capacity of solar PV has reached 494.3GW, which is expected to increase by more than 1 TW between 2019 and 2030 (source: Global Data). It is estimated that most of the new capacity during this period will come from China, India and other Asia Pacific countries. With the rapid growth of installed capacity and the improvement of technical level, the average cost of establishing solar PV is significantly reduced, but the gap between countries is still large. The reduction of production costs and the support of the government's policies have reduced the average system price of solar PV. In 2010, the average capital cost of global solar photovoltaic power stations was 4162 US dollars/kilowatt, which decreased to 1240 US dollars/kilowatt in 2018. According to the cost estimates of some countries, it is estimated that the cost will further decrease to 997 US dollars/kilowatt by 2030. The figure below shows the price trend of the top five solar photovoltaic countries and photovoltaic average system in the world from 2010 to 2018.
Solar energy is the cleanest and richest renewable energy available. Solar photovoltaic cells or panels are devices that convert solar energy into electrical energy. Intensive development and large-scale production of solar panels have begun in this new millennium. In 2018, the global installed capacity of solar PV has reached 494.3GW, which is expected to increase by more than 1 TW between 2019 and 2030 (source: Global Data). It is estimated that most of the new capacity during this period will come from China, India and other Asia Pacific countries. With the rapid growth of installed capacity and the improvement of technical level, the average cost of establishing solar PV is significantly reduced, but the gap between countries is still large. The reduction of production costs and the support of the government's policies have reduced the average system price of solar PV. In 2010, the average capital cost of global solar photovoltaic power stations was 4162 US dollars/kilowatt, which decreased to 1240 US dollars/kilowatt in 2018. According to the cost estimates of some countries, it is estimated that the cost will further decrease to 997 US dollars/kilowatt by 2030. The figure below shows the price trend of the top five solar photovoltaic countries and photovoltaic average system in the world from 2010 to 2018.
In order to remain competitive, photovoltaic and power system manufacturers are constantly seeking new technologies. Power conversion efficiency, inverter weight/size and material cost are all factors to be considered in the design. The power and level of the solar converter vary depending on the application& nbsp; Residential power consumption is generally below 10kW, and commercial power consumption is generally between 10kW and 70kW. The power of public utility scale power plants is more than 70 kilowatts. At present, most systems still use the maximum bus voltage of 1000V, but recently developed large-scale solar power plants have begun to increase the PV voltage from 1000V to 1500V. Higher voltage can reduce semiconductor and copper losses and further improve power system efficiency. For 1500V bus voltage, three-level boost and inverter topology is the only effective solution using 1200V switching devices.
SiC SBD has been widely used in the design of photovoltaic boost converter, and SiC MOSFETs have also been used in the development of many high-performance inverters. The following are two topology examples for PV inverter design.
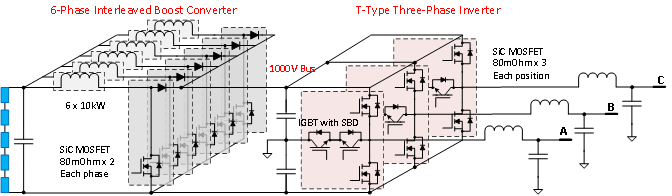
Figure 2& nbsp; Inverter solution using TO-247 SiC MOSFET
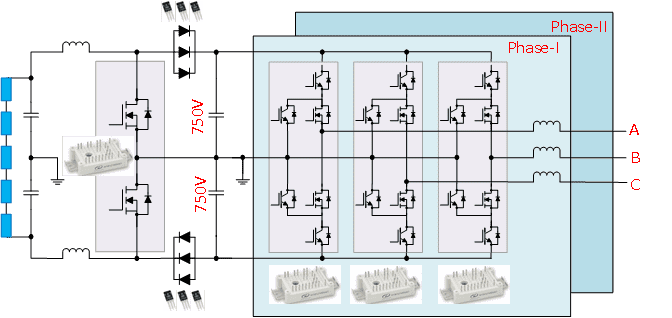
Figure 3; Use TO-247 SiC MOSFET and IV1E SiC; Module's 150kW Inverter Solution
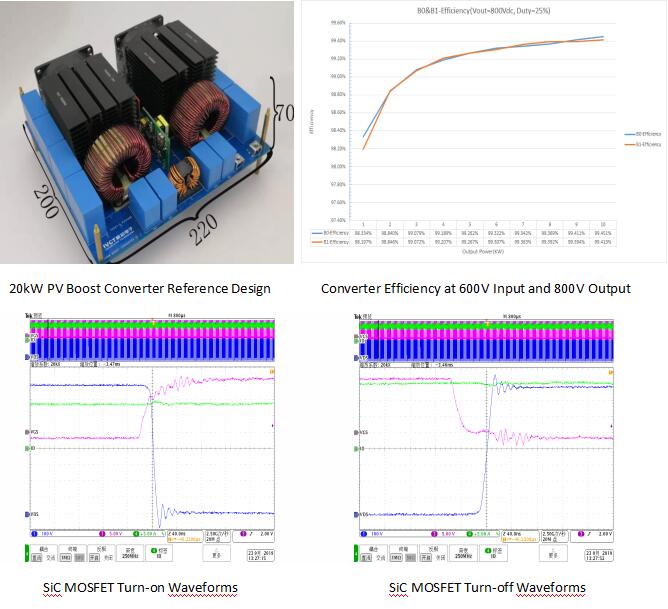
IVCT has developed a 20kW staggered boost converter to demonstrate SiC SBD and MOSFET performance. The converter uses four 80mOhm 1200V IV1Q12080T4 MOSFTEs and four 10A 1200V IV1D12010T3 diodes. At 65kHz, the input voltage is 600V, the output voltage is 800V, and the efficiency reaches 99.4%& nbsp; MOSFET is driven by SiC MOSFET special driver chip IVCR1401. The waveform below shows the clean rising and falling edges of Vds.
Solar energy is the cleanest and richest renewable energy available. Solar photovoltaic cells or panels are devices that convert solar energy into electrical energy. Intensive development and large-scale production of solar panels have begun in this new millennium. In 2018, the global installed capacity of solar PV has reached 494.3GW, which is expected to increase by more than 1 TW between 2019 and 2030 (source: Global Data). It is estimated that most of the new capacity during this period will come from China, India and other Asia Pacific countries. With the rapid growth of installed capacity and the improvement of technical level, the average cost of establishing solar PV is significantly reduced, but the gap between countries is still large. The reduction of production costs and the support of the government's policies have reduced the average system price of solar PV. In 2010, the average capital cost of global solar photovoltaic power stations was 4162 US dollars/kilowatt, which decreased to 1240 US dollars/kilowatt in 2018. According to the cost estimates of some countries, it is estimated that the cost will further decrease to 997 US dollars/kilowatt by 2030. The figure below shows the price trend of the top five solar photovoltaic countries and photovoltaic average system in the world from 2010 to 2018
In order to remain competitive, photovoltaic and power system manufacturers are constantly seeking new technologies. Power conversion efficiency, inverter weight/size and material cost are all factors to be considered in the design. The power and level of the solar converter vary depending on the application& nbsp; Residential power consumption is generally below 10kW, and commercial power consumption is generally between 10kW and 70kW. The power of public utility scale power plants is more than 70 kilowatts. At present, most systems still use the maximum bus voltage of 1000V, but recently developed large-scale solar power plants have begun to increase the PV voltage from 1000V to 1500V. Higher voltage can reduce semiconductor and copper losses and further improve power system efficiency. For 1500V bus voltage, three-level boost and inverter topology is the only effective solution using 1200V switching devices.
SiC SBD has been widely used in the design of photovoltaic boost converter, and SiC MOSFETs have also been used in the development of many high-performance inverters. The following are two topology examples for PV inverter design.
IVCT has developed a 20kW staggered boost converter to demonstrate SiC SBD and MOSFET performance. The converter uses four 80mOhm 1200V IV1Q12080T4 MOSFTEs and four 10A 1200V IV1D12010T3 diodes. At 65kHz, the input voltage is 600V, the output voltage is 800V, and the efficiency reaches 99.4%& nbsp; MOSFET is driven by SiC MOSFET special driver chip IVCR1401. The waveform below shows the clean rising and falling edges of Vds.
Copyright © 2025 :FOSEEN TECHNOLOGY (SHENZHEN) CO., LTD
Support:wanet